html5指南-2.如何操作document metadata
編輯:HTML5詳解
1.操作Document Metadata
首先我們來看看相關的屬性:
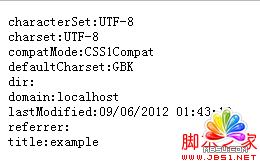
characterSet:獲取當前document的編碼方式,該屬性為只讀;
charset:獲取或者設置當前document的編碼方式;
compatMode:獲取當前document的兼容模式;
cookie:獲取或者設置當前document的cookIE對象;
defaultCharset:獲取浏覽器默認的編碼方式;
defaultVIEw:獲取當前當前document的window對象;
dir:獲取或者設置當前document的文本對齊方式;
domain:獲取或者設置當前document的domian值;
implementation:提供所支持的dom特性的信息;
lastModifIEd:獲取document最後的修改時間(如果沒有最後修改時間,則返回當前時間);
location:提供當前document的url信息;
readyState:返回當前document的狀態,該屬性是只讀屬性;
referrer: 返回連接到當前document的document url信息;
title:獲取或者設置當前document的title。
來看下面的例子:
復制代碼代碼如下:www.mb5u.com
<!DOCTYPE Html>
<Html>
<head>
<title>example</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/Javascript">
document.writeln('<pre>');
document.writeln('characterSet:' + document.characterSet);
document.writeln('charset:' + document.charset);
document.writeln('compatMode:' + document.compatMode);
document.writeln('defaultCharset:' + document.defaultCharset);
document.writeln('dir:' + document.dir);
document.writeln('domain:' + document.domain);
document.writeln('lastModified:' + document.lastModifIEd);
document.writeln('referrer:' + document.referrer);
document.writeln('title:' + document.title);
document.write('</pre>');
</script>
</body>
</Html>
結果(不同浏覽器顯示的結果可能不一樣):
2.如何理解兼容模式
compatMode屬性告訴你浏覽器是如何處理當前document的。有太多不標准的html了,浏覽器會試圖顯示這些頁面,即使他們不符合Html規范。有些內容依賴於早先浏覽器大戰時所存在的獨特的特性,而這些屬性石不符合規范的。compatMode會返回一個或兩個值,如下:
CSS1Compat:document符合一個有效的Html規范(不一定是Html5/">Html5,驗證的Html4頁面同樣返回這個值);
BackCompat:document包含不符合規范的特性,觸發了兼容模式。
3.使用Location對象
document.location返回一個Location對象,向你提供細粒度的document的地址信息,同時允許你導航到其他document。
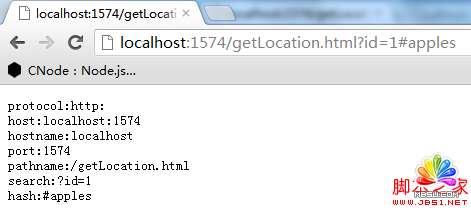
protocol:獲取或者設置document url的協議;
host:獲取或者設置document url的主機信息;
href:獲取或者設置document的地址信息;
hostname:獲取或者設置document的主機名;
search:獲取或者設置document url查詢部分的信息;
hash:獲取或者設置document url hash部分的信息;
assign(<url>):導航到一個指定url;
replace(<url>):移除當前document,導航到指定的url;
reload():重新加載當前document;
resolveURL(<url>):將相對路徑變為絕對路徑。
來看下面的例子:
復制代碼代碼如下:www.mb5u.com
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xHtml1-transitional.dtd">
<Html XMLns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xHtml">
<head>
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/Javascript">
document.writeln('<pre>');
document.writeln('protocol:' + document.location.protocol);
document.writeln('host:' + document.location.host);
document.writeln('hostname:' + document.location.hostname);
document.writeln('port:' + document.location.port);
document.writeln('pathname:' + document.location.pathname);
document.writeln('search:' + document.location.search);
document.writeln('hash:' + document.location.hash);
document.writeln('</pre>');
</script>
</body>
</Html>
結果:
4.讀寫cookIE
通過cookie屬性,可以對document的cookIE進行新增,修改和讀取操作。如下例:
復制代碼代碼如下:www.mb5u.com
<!DOCTYPE Html>
<Html>
<head>
<title>Example</title>
<meta name="author" content="Adam Freeman" />
<meta name="description" content="A simple example" />
</head>
<body>
<p id="cookIEdata">
</p>
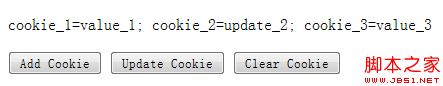
<button id="write">
Add CookIE</button>
<button id="update">
Update CookIE</button>
<button id="clear">
Clear CookIE</button>
<script type="text/Javascript">
var cookIECount = 0;
document.getElementById('update').onclick = updateCookIE;
document.getElementById('write').onclick = createCookIE;
document.getElementById('clear').onclick = clearCookIE;
readCookIEs();
function readCookIEs() {
document.getElementById('cookIEdata').innerHtml = !document.cookie ? '' : document.cookIE;
}
function updateCookIE() {
document.cookie = 'cookie_' + cookieCount + '=update_' + cookIECount;
readCookIEs();
}
function createCookIE() {
cookIECount++;
document.cookie = 'cookie_' + cookieCount + '=value_' + cookIECount;
readCookIEs();
}
function clearCookIE() {
var exp = new Date();
exp.setTime(exp.getTime() - 1);
var arrStr = document.cookIE.split("; ");
for (var i = 0; i < arrStr.length; i++) {
var temp = arrStr[i].split("=");
if (temp[0]) {
document.cookIE = temp[0] + "=;expires=" + exp.toGMTString();
};
}
cookIECount = 0;
readCookIEs();
}
</script>
</body>
</Html>
結果:
5.理解ReadyState
document.readyState幫助你了解頁面加載和解析過程中,頁面所處的當前狀態。需要記住的一點是,浏覽器當遇到script元素時會立即執行,除非你使用defer屬性延時腳本的執行。readyState有三個值代表不同的狀態。
loading:浏覽器正在加載和執行document;
interactive:docuent已經完成解析,但是浏覽器正在加載其他外部資源(media,圖片等);
complete:頁面解析完成,外部資源在家完畢。
在浏覽器整個加載和解析的過程中,readyState的值會從loading,interactive和complete逐個改變。當結合readystatechange事件(readyState狀態改變時觸發)使用,readyState會變得相當有價值。
復制代碼代碼如下:www.mb5u.com
<!DOCTYPE Html>
<Html>
<head>
<title>Example</title>
<meta name="author" content="Adam Freeman" />
<meta name="description" content="A simple example" />
<script>
document.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (document.readyState == "interactive") {
document.getElementById("pressme").onclick = function () {
document.getElementById("results").innerHtml = "Button Pressed";
}
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<button id="pressme">
Press Me</button>
<pre id="results"></pre>
</body>
</Html>
上面的代碼使用readystatechange事件實現了延時執行的效果,只有當頁面上整個頁面解析接觸之後readystate的值才會變成interactive,這時再為pressme按鈕綁定click事件。這樣操作可以確保所需要的Html元素都存在,防止錯誤發生。
6.獲取dom屬性實現的信息
document.implementation屬性幫助你了解浏覽器對dom屬性的實現情況。該屬性返回DOMImplementation對象,對象包含hasFeature方法,你可以通過該方法了解浏覽器對某屬性的實現情況。
復制代碼代碼如下:www.mb5u.com
<!DOCTYPE Html>
<Html>
<head>
<title>Example</title>
<meta name="author" content="Adam Freeman" />
<meta name="description" content="A simple example" />
</head>
<body>
<script>
var features = ["Core", "Html", "CSS", "Selectors-API"];
var levels = ["1.0", "2.0", "3.0"];
document.writeln("<pre>");
for (var i = 0; i < features.length; i++) {
document.writeln("Checking for feature: " + features[i]);
for (var j = 0; j < levels.length; j++) {
document.write(features[i] + " Level " + levels[j] + ": ");
document.writeln(document.implementation.hasFeature(features[i], levels[j]));
}
}
document.write("</pre>")
</script>
</body>
</Html>
效果:

小編推薦
熱門推薦