AJAX (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML,異步的 JavaScript 和 XML)。它不是新的編程語言,而是一種使用現有標准的新方法,是在不重新加載整個頁面的情況下與服務器交換數據並更新部分網頁的藝術。
那麼,讓我們一起走進AJax的世界吧。
基礎語法
學習Ajax之前,我們要明確自己的需求,那就是在不刷新頁面的前提下實現異步的與服務器進行交互,更新頁面信息。使用Ajax其實也是很簡單的,我們只需要遵循一定的步驟即可。
•創建Ajax對象(原生的需要判斷當前浏覽器的類型)
•設置回調函數 (完成與服務器的交互之後所觸發的函數)
•打開請求,並發送。(根據請求方式的不同,代碼書寫稍有不同)
•客戶端獲得反饋數據,更新頁面
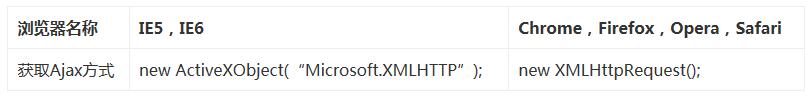
獲取Ajax對象
不同的浏覽器對Ajax的支持是不一致的,所以我們要區別的對待。
設置回調函數
設置回調函數的目的就是在Ajax完成與服務器的交互之後,將獲取到的數據信息,添加到頁面上。
通常我們會指定onreadystatechange函數作為我們的回調處理函數。
相關於Ajax與服務器交互有如下狀態信息供我們在編碼的過程找中參考。
.readystate
關於加載狀態有如下幾個常用的數值:
•0: 請求未初始化
•1: 服務器連接已建立
•2: 請求已接收
•3: 請求處理中
•4: 請求已完成,且響應已就緒
.status
加載結果的狀態信息有:
•200: “OK”
•404: “未找到此頁面”
開啟交互
一談起交互,映入腦海的就是雙方。也就是我們的ajax客戶端和服務器之間的交互。所以我們需要明確請求數據在服務器上的位置
open(method,url,async)
url的使用會根據method的不同而不同,這一點我們務必要清楚。至於asynchronous這個參數,一般來說對於數據量很小的請求可以采用false,但是建議使用true來進行異步的加載,來避免服務器壓力過大。
•GET方式
只是用這種方式很簡單,指定url在服務器上的位置即可。這裡紅色部分的理解相當的重要。我們務必指定url為請求在服務器上的位置,一般采用絕對路徑的方式。
// 對Servlet來說指定其注解上的位置即可
xmlhttp.open("GET","/Test/servlet/AjaxServlet?userinput="+str.value,true);
xmlhttp.send();
•POST方式
使用POST方式的時候,我們需要額外的多一項處理。如下例:
xmlhttp.open("POST","ajax_test.asp",true);
xmlhttp.setRequestHeader("Content-type","application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
// 在send方法中指定要傳輸的參數信息即可
xmlhttp.send("fname=Bill&lname=Gates");
客戶端更新頁面
對於Ajax來說,顧名思義。是采用xml形式來傳輸數據的。但是目前而言,這不再是唯一的一種形式了。那麼我們怎麼將獲取到的數據更新到網頁上呢?有如下兩種方式。
•如果來自服務器的響應並非 XML,請使用 responseText 屬性。
document.getElementById("myDiv").innerHTML=xmlhttp.responseText;
•如果來自服務器的響應是 XML,而且需要作為 XML 對象進行解析,請使用 responseXML 屬性:
xmlDoc=xmlhttp.responseXML;
txt="";
x=xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("ARTIST");
for (i=0;i<x.length;i++)
{
txt=txt + x[i].childNodes[0].nodeValue + "<br />";
}
document.getElementById("myDiv").innerHTML=txt;
實例體驗
了解了這些基礎語法之後,我們就可以在實際的開發中簡單的應用了。為了更好的完成此次實驗,我先做了一個簡單的JavaWeb,來處理我們的Ajax請求。
使用Servlet方式
AjaxServlet.java
package one;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
/**
* Servlet implementation class AjaxServlet
*/
@WebServlet("/AjaxServlet")
public class AjaxServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/**
* @see HttpServlet#HttpServlet()
*/
public AjaxServlet() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
/**
* @see HttpServlet#doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse
* response)
*/
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//response.getWriter().append("Served at: ").append(request.getContextPath());
String userinput = request.getParameter("userinput");
System.out.println("客戶端連接!");
System.out.println("請求信息為:" + userinput);
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
if(userinput.equals("") || userinput.length()<6) {
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
response.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/html;charset=utf-8");
out.write("<h3>the length of input string must be more than 6!</h3>");
}else{
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
response.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/html;charset=utf-8");
out.println("<h3>Correct!</h3>");
}
out.close();
}
/**
* @see HttpServlet#doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse
* response)
*/
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
doGet(request, response);
}
}
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0"> <display-name>Test</display-name> <welcome-file-list> <welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file> <welcome-file>index.htm</welcome-file> <welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.html</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.htm</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.jsp</welcome-file> </welcome-file-list> <servlet> <servlet-name>AjaxServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>one.AjaxServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>AjaxServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/servlet/AjaxServlet</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
ajax.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Ajax測試</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<h2>AJAX Test</h2>
<input type="text" name="userinput" placeholder="用戶輸入,Ajax方式獲得數據" onblur="getResult(this)">
<br>
<span id="ajax_result"></span>
<script>
getResult = function(str){
var httpxml;
if(0 == str.value.length) {
document.getElementById("ajax_result").innerHTML = "Nothing";
}
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
}else{
xmlhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
xmlhttp.onreadystatechange = function(){
if(4 == xmlhttp.readyState && 200 == xmlhttp.status) {
document.getElementById("ajax_result").innerHTML = xmlhttp.responseText;
}
}
xmlhttp.open("GET","/Test/servlet/AjaxServlet?userinput="+str.value,true);
xmlhttp.send();
}
</script>
</div>
</body>
</html>
實驗結果
•長度小於6時:

•長度大於等於6:

使用JSP方式
receiveParams.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%
//接收參數
String userinput = request.getParameter("userinput");
//控制台輸出表單數據看看
System.out.println("userinput =" + userinput);
//檢查code的合法性
if (userinput == null || userinput.trim().length() == 0) {
out.println("code can't be null or empty");
} else if (userinput != null && userinput.equals("admin")) {
out.println("code can't be admin");
} else {
out.println("OK");
}
%>
ajax.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Ajax測試</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<h2>AJAX Test</h2>
<input type="text" name="userinput" placeholder="用戶輸入,Ajax方式獲得數據" onblur="getResult(this)">
<br>
<span id="ajax_result"></span>
<script>
getResult = function(str){
var httpxml;
if(0 == str.value.length) {
document.getElementById("ajax_result").innerHTML = "Nothing";
}
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
}else{
xmlhttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
xmlhttp.onreadystatechange = function(){
if(4 == xmlhttp.readyState && 200 == xmlhttp.status) {
document.getElementById("ajax_result").innerHTML = xmlhttp.responseText;
}
}
//xmlhttp.open("GET","/Test/servlet/AjaxServlet?userinput="+str.value,true);
xmlhttp.open("GET","receiveParams.jsp?userinput="+str.value,true);
xmlhttp.send();
}
</script>
</div>
</body>
</html>
效果一致。
JQuery 中的Ajax
前面介紹的是原生的Ajax實現方式,我們需要做的工作還是很多的,而JQuery幫助我們完成了平台無關性的工作,我們只需要專注於業務邏輯的開發即可。直接用jquery的.post或者.get或者.ajax方法,更方便更簡單,js代碼如下:
•.POST方式
$.post("./newProject",{newProjectName:project_name},
function(data,status){
//alert("data:" + data + "status:" + status);
if(status == "success"){
var nodes = data.getElementsByTagName("project");
//alert(nodes[0].getAttribute("name"));
for(var i = 0;i < nodes.length;i ++){
$("#project_items").append("<option value=\"" + (i+1) + "\">" + nodes[i].getAttribute("name") + "</option>");
}
}
})
•.ajax方式
$(function(){
//按鈕單擊時執行
$("#testAjax").click(function(){
//Ajax調用處理
$.ajax({
type: "POST",
url: "test.php",
data: "name=garfield&age=18",
success: function(data){
$("#myDiv").html('<h2>'+data+'</h2>');
}
});
});
});
•.get方式
$(document).ready(function(){
$("#bt").click(function(){
$.get("mytest/demo/antzone.txt",function(data,status){
alert("Data:"+data+"\nStatus:"+status);
})
})
})
總結
今天的演示對於實際開發的過程中,服務器端的用戶輸入數據驗證,或者即時更新頁面而又減少網絡流量是非常的有必要的。而且用處也很廣泛,還能有效的提升用戶體驗。
這次的案例,就當是拋磚引玉,給你的應用也添加上異步加載吧。
- 上一頁:ajax同步驗證單號是否存在的方法
- 下一頁:Ajax技術組成與核心原理分析