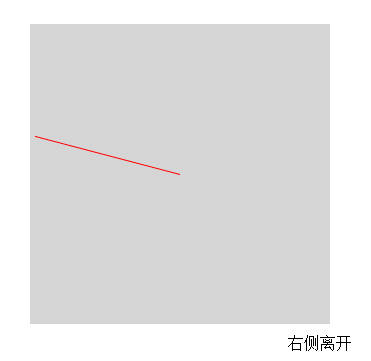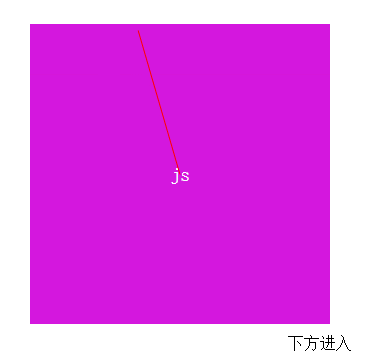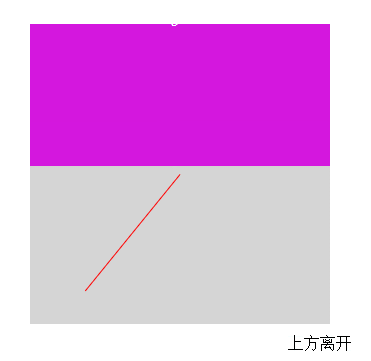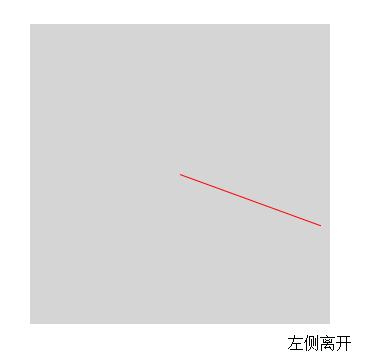
最終效果
這裡的關鍵主要是判斷鼠標是從哪個方向進入和離開的
$("li").on("mouseenter mouseleave",function(e) {
var w = this.offsetWidth;
var h = this.offsetHeight;
var x = e.pageX - this.getBoundingClientRect().left - w/2;
var y = e.pageY - this.getBoundingClientRect().top - h/2;
var direction = Math.round((((Math.atan2(y, x) * 180 / Math.PI) + 180) / 90) + 3) % 4; //direction的值為“0,1,2,3”分別對應著“上,右,下,左”
var eventType = e.type;
var res = Math.atan2(y, x) / (Math.PI / 180) + 180 ;
$('.line').css('transform','rotate('+ res +'deg)');
// console.log(((Math.atan2(y, x) * 180 / Math.PI) + 180));
// console.log(Math.round((Math.atan2(y, x) / (Math.PI / 180) + 180) / 90 + 3) % 4);
var dirName = new Array('上方','右側','下方','左側');
$('.res').text(res + 'deg');
if(eventType == 'mouseenter'){
$('.res').text(dirName[direction]+'進入');
animationIn(direction);
}else{
$('.res').text(dirName[direction]+'離開');
animationOut(direction);
}
});
上面代碼的重點主要是在direction的值的計算
Math.atan2(y,x) 返回-PI 到 PI 之間的值(負180°到正180°),是從 X 軸正向逆時針旋轉到點 (x,y) 時經過的角度 這裡的結果是一個弧度值。那如何把這個值轉換為角度呢
我們可以先算出一個角度的弧度值(Math.PI / 180) ,然後用上面計算出來的結果除以一度的弧度值
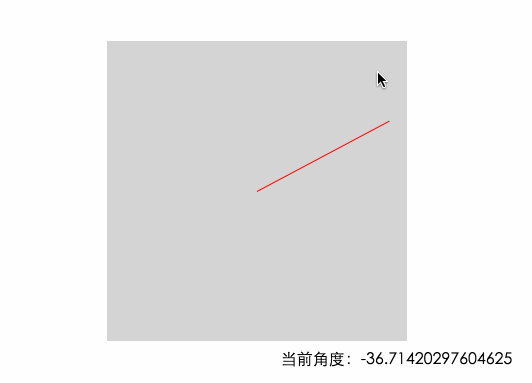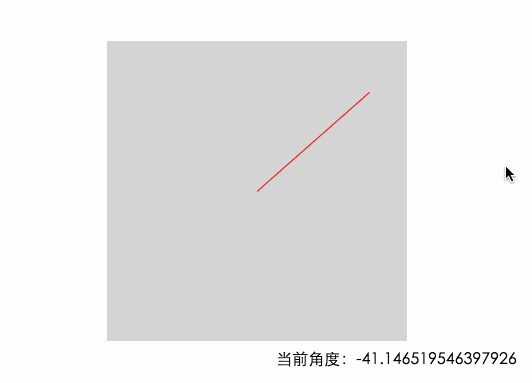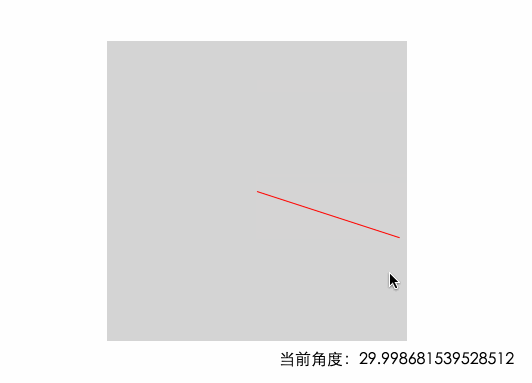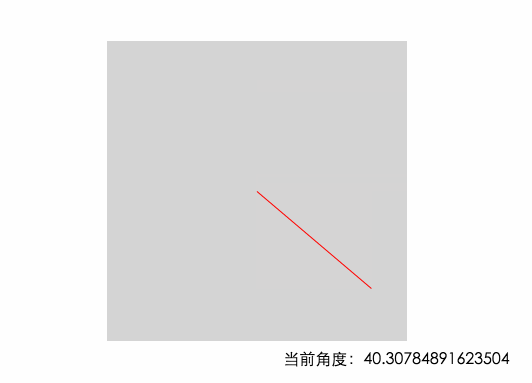
從上圖可以看出,當鼠標從右邊進入的時候,角度是在-45°~45°之間的 底部是45~135 左邊135~180&-180~-135 頂部是 -135 ~ -45
因為上面計算出來的結果不符合我們的習慣,並且負值在計算的時候會影響正確性,現在我們給這個結果加上180 讓角度范圍變成我們習慣的0~360°。當加上180之後 0°的位置就在左邊的中間了
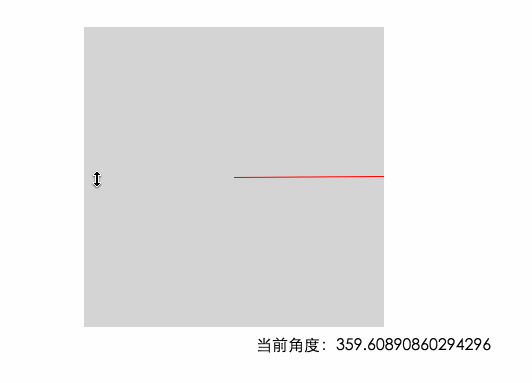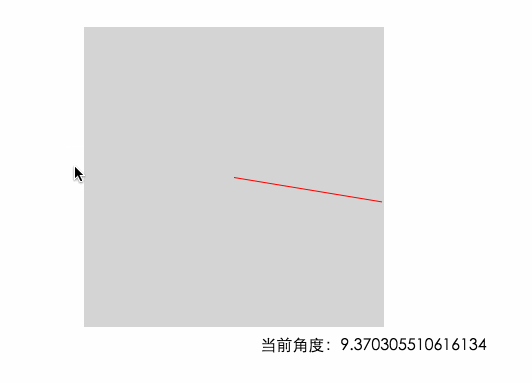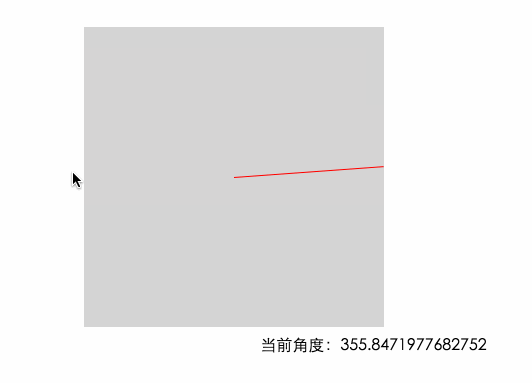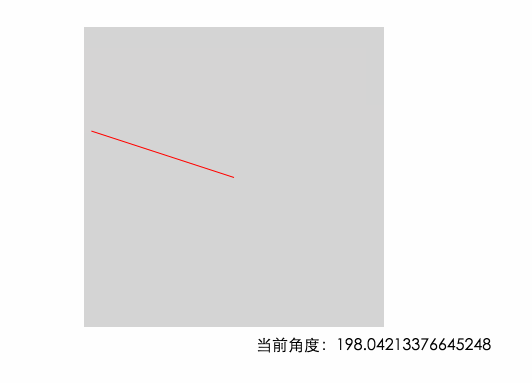
0度的位置
所以現在的范圍變成了
0~44 & 360~315 左邊
45~134 上邊
135~224 右邊
225~314 下邊
我們再繼續轉換,現在我們把算出來的角度除以90,然後四捨五入,可以使得45°為分界線
上邊算出來的結果為1
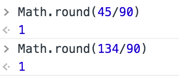
上邊
右邊算出來的結果為2
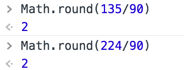
右邊
下邊算出來的結果為3
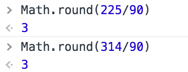
下邊
左邊算出來的結果有兩種 0~44肯定是為0的 315~360 為4
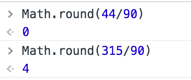
左邊
現在算出來的結果一共有5個值(左邊2個,其他三個面各一個)。下面我們再精簡一下結果,我們給每次的結果都加上3,然後和4取余
左邊加3之後就是3和7,然後取余後為3
上邊加3之後為4,取余後為0
右邊加3為5,取余為1
下邊加3為6,取余為2
我們最終的結果就是 0->上邊 1->右邊 2->下邊 3->左邊 然後我們通過控制left和top就可以實現上面的效果了
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
html,
body {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
ul {
list-style: none;
position: relative;
width: 600px;
width: 100%;
}
ul> li {
margin: 50px auto;
position: relative;
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: black;
overflow: hidden;
}
ul> li .bg {
position: absolute;
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
left: -100%;
top: 0;
background-color: red;
text-align: center;
line-height: 300px;
color: blue;
font-size: 150px;
}
.line {
position: absolute;
width: 50%;
height: 1px;
background: red;
right: 0;
top: 50%;
transition: all .3s;
transform-origin: left;
}
.res {
text-align: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li>
<div class="bg">
SB
</div>
</li>
</ul>
<div class="res"></div>
<script src="js/jquery-3.1.1.js"></script>
<script>
$("li").on("mouseenter mouseleave", function(e) {
var $bg = $(this).find('.bg');
var w = this.offsetWidth; //獲取元素寬度
var h = this.offsetHeight; //獲取元素高度
var toTop = this.getBoundingClientRect().top + document.body.scrollTop; //兼容滾動條
var x = e.pageX - this.getBoundingClientRect().left - w / 2; //獲取當前鼠標的x軸位置(相對於這個li的中心點)
var y = e.pageY - toTop - h / 2; ////獲取當前鼠標的y軸位置(相對於這個li的中心點)
var direction = Math.round((((Math.atan2(y, x) * 180 / Math.PI) + 180) / 90) + 3) % 4; //direction的值為“0,1,2,3”分別對應著“上,右,下,左”
var eventType = e.type;
var res = Math.atan2(y, x) / (Math.PI / 180) + 180;
$('.line').css('transform', 'rotate(' + res + 'deg)');
var dirName = new Array('上方', '右側', '下方', '左側');
if(eventType == 'mouseenter') {
$('.res').text(dirName[direction] + '進入');
animationIn(direction, $bg);
} else {
$('.res').text(dirName[direction] + '離開');
animationOut(direction, $bg);
}
});
function animationIn(direction, ele) {
switch(direction) {
case 0:
ele.css({
left: 0,
top: '-100%'
}).animate({
top: 0
}, 300);
break;
case 1:
ele.css({
left: '100%',
top: 0
}).animate({
left: 0
}, 300);
break;
case 2:
ele.css({
left: 0,
top: '100%'
}).animate({
top: 0
}, 300);
break;
case 3:
ele.css({
left: '-100%',
top: 0
}).animate({
left: 0
}, 300);
break;
}
}
function animationOut(direction, ele) {
switch(direction) {
case 0:
ele.animate({
top: '-100%'
}, 300);
break;
case 1:
ele.animate({
left: '100%'
}, 300);
break;
case 2:
ele.animate({
top: '100%'
}, 300);
break;
case 3:
ele.animate({
left: '-100%'
}, 300);
break;
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望本文的內容對大家的學習或者工作能帶來一定的幫助,同時也希望多多支持!