接著上一篇vue慢速入門教程學習。
4.組件使用基礎
什麼是組件?組件可以理解為可重用的自定義HTML。
可以使用一堆組件來構造大型應用,任意類型的應用界面都可以抽象為一個組件樹:
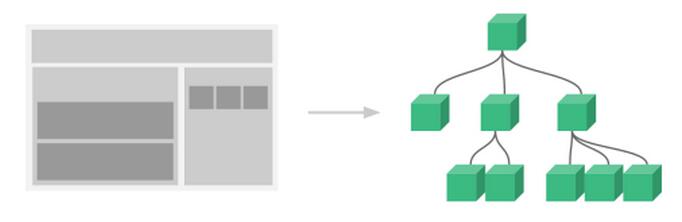
可以把組件代碼按照template、style、script的拆分方式,放置到對應的.vue文件中。
組件預定義選項中最核心的幾個:
模板(template)、初始數據(data)、接受的外部參數(props)、方法(methods)、生命周期鉤子函數(lifecycle hooks)。
4.1 基本步驟
使用組件首先需要創建構造器:
var MyComponent = Vue.extend({
// 選項...
})
要把這個構造器用作組件,需要用 Vue.component(tag, constructor) 注冊 :
// 全局注冊組件,tag 為 my-component
Vue.component('my-component', MyComponent)
然後使用:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="xxx">
<my-component></my-component>
</div>
</body>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var myComponent = Vue.extend({
template: '<p>9898不得了!</p>'
});
Vue.component('my-component', myComponent);
new Vue({
el: '#xxx'
});
</script>
</html>
其中,
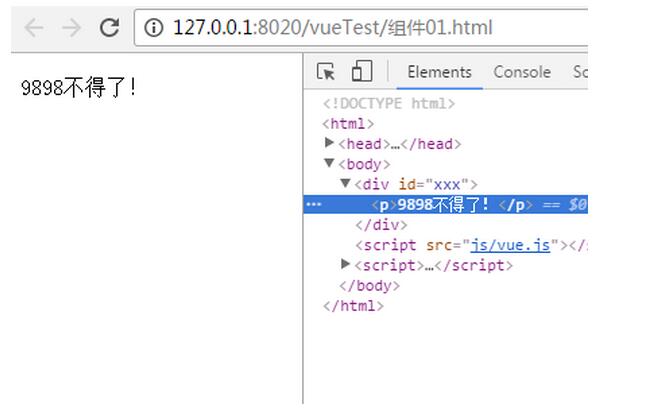
Vue.component('my-component', MyComponent)這種是全局注冊,第一個參數是注冊組件的名稱,第二個參數是組件的構造函數;
選項對象的template屬性用於定義組件要渲染的HTML;
組件的模板替換了自定義元素,自定義元素的作用只是作為一個掛載點。組件掛載在vue實例上才會生效。
對於自定義標簽名字,Vue.js 不強制要求遵循 W3C 規則(小寫,並且包含一個短槓),為了避免不必要的事端盡管遵循這個規則。
4.2 局部注冊
用實例選項 components 注冊:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="xxx">
<my-component></my-component>
</div>
</body>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var myComponent = Vue.extend({
template: '<p>9898不得了!</p>'
});
// Vue.component('my-component', myComponent);
new Vue({
el: '#xxx',
components: {
'my-component': myComponent
}
});
</script>
</html>
也可以在組件中定義並使用其他組件:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="example">
<xx-component></xx-component>
</div>
</body>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var Child = Vue.extend({
template: '<div>i am zai</div>',
replace: true
})
var Parent = Vue.extend({
template: '<p>i am baba</p><br/><wa></wa>',
components: {
// <xx-component>只能用在父組件模板內
'wa': Child
}
})
// 創建根實例
new Vue({
el: '#example',
components: {
'xx-component': Parent
}
})
</script>
</html>
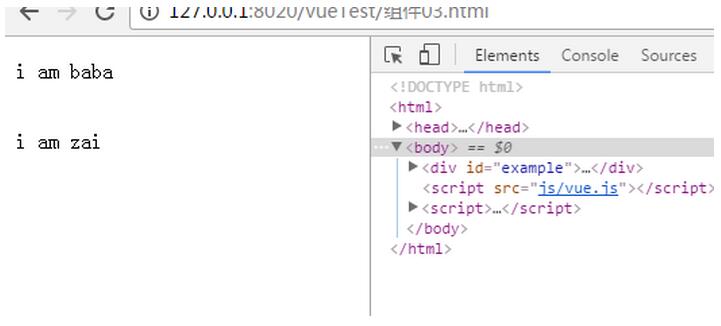
其中,子組件只能在父組件的template中使用。
另外,有簡化的寫法,Vue在背後會自動地調用Vue.extend():
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="xxx">
<my-component-continue></my-component-continue>
</div>
</body>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
// 局部注冊的簡化寫法
var vm2 = new Vue({
el: '#xxx',
components: {
'my-component': {
template: '<div>9898不得了!</div>'
},
'my-component-continue': {
template: '<div>糧食大豐收!</div>'
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
4.3 組件選項問題
在定義組件的選項時,data和el選項必須使用函數。
如果data選項指向某個對象,這意味著所有的組件實例共用一個data。
所以應當使用一個函數作為 data 選項,讓這個函數返回一個新對象:
Vue.component('my-component', {
data: function(){
return {a : 1}
}
})
同理,el 選項用在 Vue.extend() 中時也須是一個函數。
5.數據傳遞
Vue.js組件之間有三種數據傳遞方式:
props
組件通信
slot
5.1 props
“props”是組件數據的一個字段,期望從父組件傳下來數據。因為組件實例的作用域是孤立的,所以子組件需要顯式地用props選項來獲取父組件的數據。
Props選項可以是字面量、表達式、綁定修飾符。
5.1.1 字面量
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<child msg="hello!"></child>
<script src="js/vue.js" type="text/javascript" charset="utf-8"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.component('child', {
// 聲明 props
props: ['msg'],
// prop 可以用在模板內
// 可以用 `this.msg` 設置
template: '<span>{{ msg }}你困嗎</span>'
})
new Vue({
el: 'body'
})
</script>
</body>
</html>

HTML 特性不區分大小寫。名字形式為 camelCase 的 prop 用作特性時,需要轉為 kebab-case(短橫線隔開):
Vue.component('child', {
// camelCase in JavaScript
props: ['myMessage'],
template: '<span>{{ myMessage }}</span>'
})
<!-- kebab-case in HTML -->
<child my-message="hello!"></child>
5.1.2 動態
類似於用 v-bind 綁定 HTML 特性到一個表達式,也可以用 v-bind 綁定動態 Props 到父組件的數據。每當父組件的數據變化時,也會傳導給子組件。比如醬:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
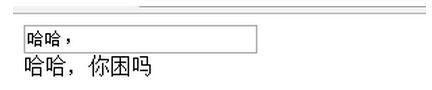
<div>
<input v-model="parentMsg">
<br>
<child :my-message="parentMsg"></child>
</div>
<script src="js/vue.js" type="text/javascript" charset="utf-8"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.component('child', {
props: ['myMessage'],
template: '<span>{{ myMessage }}你困嗎</span>'
})
new Vue({
el: 'body',
data:{
parentMsg:''
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
當我在input裡面輸入哈哈的時候:
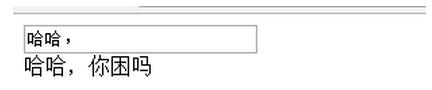
5.1.3 綁定類型
可以使用綁定修飾符:
.sync,雙向綁定
.once,單次綁定
<!-- 默認為單向綁定 --> <child :msg="parentMsg"></child> <!-- 雙向綁定 --> <child :msg.sync="parentMsg"></child> <!-- 單次綁定 --> <child :msg.once="parentMsg"></child>
prop 默認是單向綁定:當父組件的屬性變化時,將傳導給子組件,但是反過來不會。
不過需要注意的是:如果 prop 是一個對象或數組,是按引用傳遞。在子組件內修改它會影響父組件的狀態,不管是使用哪種綁定類型。
示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<table>
<tr>
<th colspan="3">父組件數據</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>name</td>
<td>{{ name }}</td>
<td><input type="text" v-model="name" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>age</td>
<td>{{ age }}</td>
<td><input type="text" v-model="age" /></td>
</tr>
</table>
<my-component v-bind:my-name.sync="name" v-bind:my-age="age"></my-component>
</div>
<template id="myComponent">
<table>
<tr>
<th colspan="3">子組件數據</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>my name</td>
<td>{{ myName }}</td>
<td><input type="text" v-model="myName" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>my age</td>
<td>{{ myAge }}</td>
<td><input type="text" v-model="myAge" /></td>
</tr>
</table>
</template>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
name: 'k',
age: 24
},
components: {
'my-component': {
template: '#myComponent',
props: ['myName', 'myAge']
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
上面這段設置了名字雙向,年齡單向:

以下是一個大神的綜合示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<table>
<tr>
<th colspan="3">父組件數據</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>name</td>
<td>{{ name }}</td>
<td><input type="text" v-model="name" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>age</td>
<td>{{ age }}</td>
<td><input type="text" v-model="age" /></td>
</tr>
</table>
<my-component v-bind:my-name.sync="name" v-bind:my-age="age"></my-component>
</div>
<template id="myComponent">
<table>
<tr>
<th colspan="3">子組件數據</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>my name</td>
<td>{{ myName }}</td>
<td><input type="text" v-model="myName" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>my age</td>
<td>{{ myAge }}</td>
<td><input type="text" v-model="myAge" /></td>
</tr>
</table>
</template>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
name: 'k',
age: 24
},
components: {
'my-component': {
template: '#myComponent',
props: ['myName', 'myAge']
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
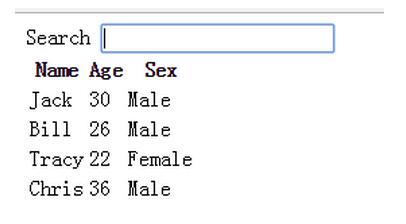
可以檢索:
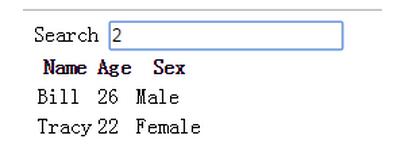
其中,{{ col | capitalize}}過濾,首字母大寫。
<tr v-for="entry in data | filterBy filterKey">
<td v-for="col in columns">
{{entry[col]}}
</td>
</tr>
過濾搜索關鍵詞;
雙循環,tr循環data條數,4行,entry表示每行;td循環columns數量,3列,col表示每列,entry[col]取具體數據。
props: {
data: Array,
columns: Array,
filterKey: String
}
驗證:父組件傳遞過來的data和columns必須是Array類型,filterKey必須是字符串類型。
驗證要求示例:
Vue.component('example', {
props: {
// 基礎類型檢測 (`null` 意思是任何類型都可以)
propA: Number,
// 多種類型 (1.0.21+)
propM: [String, Number],
// 必需且是字符串
propB: {
type: String,
required: true
},
// 數字,有默認值
propC: {
type: Number,
default: 100
},
// 對象/數組的默認值應當由一個函數返回
propD: {
type: Object,
default: function () {
return { msg: 'hello' }
}
},
// 指定這個 prop 為雙向綁定
// 如果綁定類型不對將拋出一條警告
propE: {
twoWay: true
},
// 自定義驗證函數
propF: {
validator: function (value) {
return value > 10
}
},
// 轉換函數(1.0.12 新增)
// 在設置值之前轉換值
propG: {
coerce: function (val) {
return val + '' // 將值轉換為字符串
}
},
propH: {
coerce: function (val) {
return JSON.parse(val) // 將 JSON 字符串轉換為對象
}
}
}
})
Stringtype 可以是下面原生構造器:
Number
Boolean
Function
Object
Array
type 也可以是一個自定義構造器,使用 instanceof 檢測。
當 prop 驗證失敗時,Vue 將拒絕在子組件上設置此值,如果使用的是開發版本會拋出一條警告。
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持。
參考:Vue.js——60分鐘組件快速入門(上篇)
《vue.js權威指南》