現在來系統地學習一下Vue(參考vue.js官方文檔):
Vue.js是一個構建數據驅動的web界面的庫,其目標是實現響應的數據綁定和組合的試圖組件。
Vue.js擁抱數據驅動的視圖概念,這意味著我們能在普通的HTML模板中使用特殊的用法將DOM“綁定”到底層數據。一旦創建了綁定,DOM將於數據保持同步。
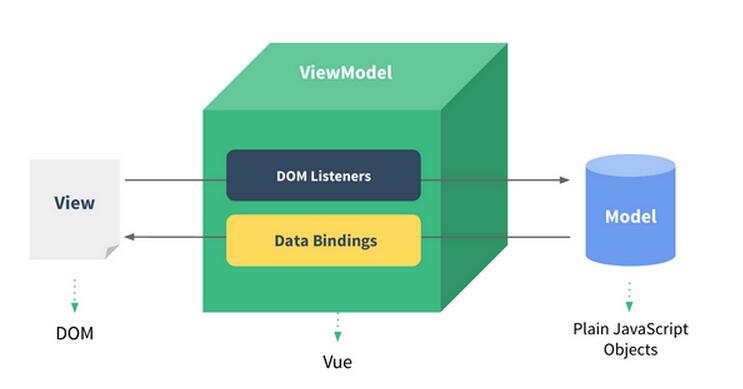
以下參考代碼與上面的模型相對應
<!-- 這是我們的 View -->
<div id="example-1">
Hello {{ name }}!
</div>
// 這是我們的 Model
var exampleData = {
name: 'Vue.js'
}
// 創建一個 Vue 實例或 "ViewModel"
// 它連接 View 與 Model
var exampleVM = new Vue({
el: '#example-1', // 在一個id為'example-1'的實體上掛載
data: exampleData // 數據流
})
通常我們會把Model寫在Vue實例當中,下面寫法與上面寫法效果一樣:
<!-- 這是我們的 View -->
<div id="example-1">
Hello {{ name }}! <!--- Vue的數據模型用{{datamodel}}包裹起來 --->
</div>
// 創建一個 Vue 實例或 "ViewModel"
// 它連接 View 與 Model<br><script>
var exampleVM = new Vue({
el: '#example-1', // 在一個id為'example-1'的實體上掛載
data: {
name: 'Vue.js'
} // 數據流
})<br></script>
這樣一段程序執行後,在#example-1這個控件中就會顯示‘Hello Vue.js!'。
下面來看看指令(Directives):
指令是特殊的帶有前綴 v- 的特性,指令的值限定為綁定表達式,比如一個if的指令:
<p v-if="greeting">hello!<p>
還有綁定指令,即將某些屬性值與一些值相綁定,比如:
<input :type = "questItem.type", :name = "questItem.name"/>
這裡省略了“v-bind”,使得input的屬性值賦值具有“計算”的效果。
計算屬性
這裡介紹一下$watch的用法,用於當一個數據需要根據其他的數據而變化時的情況:
<script><br>var vm = new Vue({
el: '#demo',
data: {
firstName: 'Foo',
lastName: 'Bar',
fullName: 'Foo Bar'
}
})<br></script>
vm.$watch('firstName', function (val) { // 當firstname改變時,立馬更新vm.fullname
this.fullName = val + ' ' + this.lastName
})
vm.$watch('lastName', function (val) { // 當lastname改變時,立馬更新vm.fullname
this.fullName = this.firstName + ' ' + val
})
在這裡,所有的數據的對象都可以通過vm.firstname等來訪問。
v-model
顧名思義,就是Vue當中的數據模型,它用來綁定Vue實例中的數據:
<!--- bi-direction bound --->
<div id="app">
<p>{{message}}</p>
<input v-model="message"> <!--Model,input輸入的數據會立即反饋到Vue實例中-->
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app', // View
data: {
message: 'Hello Vue.js'
}
})
</script>
比如要用來綁定一個表單控件,就是把選擇的值顯示出來:
<!--- 表單控件綁定-單選 --->
<div id="myselect"> // 外面這一層我一開始沒有加,然後就出錯了,el好像一般是掛載在<div>構件上
<select v-model="selected"> // data的數據類型是selected,值是選取的值
<option seleceted>A</option>
<option>B</option>
<option>C</option>
</select>
<span>Selected: {{ selected }}</span>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#myselect',
data:{
selected:[]
}
})
</script>
v-if, v-else
這個指令可以用的很靈活,比如我在表單中生成新題目,有“單選題”、“多選題”、“文本題”三種,那麼針對不同的題目應該顯示的控件有所不同,這時可以使用如下語法:
<div v-if="questItem.type === 'textarea'"> // 注意是三個等號
<textarea></textarea>
</div>
<div v=else>
<div></div>
</div>
v-for
這個用於對數組元素的遍歷,舉個例子:
<ul id="demo">
<li
v-for="item in items"
class="item-{{$index}}"> <!--- $index指的是當前數組元素在數組中的位置 --->
{{parentMessage}} - {{$index}} - {{item.message}} <!--一個view結構-->
</li>
</ul>
<button id="btn1">點擊我</button>
<script>
var demo= new Vue({
el: '#demo',
data:{
parentMessage: 'Parent',
items:[
{message: 'Foo'},
{message: 'Bar'}
]
}
})
</script>
以上代碼的意思是遍歷demo實例中的items數組,將裡面的每一個數組元素('Foo','Bar')分別在<li>標簽中顯示出來
為了避免對整個列表進行渲染,經常會使用:track-by = "$index",表示只對當前數組元素進行操作。
至此,關於Vue的最基本的東西已經介紹完,需要更多的API資料可以參考: http://cn.vuejs.org/api/
Vue文件的結構以及數據流的控制
在vue文件中,我們經常可以看到這樣的格式:
<template>
<div> </div>
</template>
<script>
export default{
data(){ ...
},
methods:{ // 自定義方法,可對data進行處理
method1(){ ... }
...
},
components: { ... }
vuex: {
getters:{ // 獲取store的數據
questionnaire: state => state.currentQuestionnaire
}
actions: { //用來分發數據容器store中mutations方法
action1(){ dispatch("SET_QUEST", item) } // dispatch用來調用父組件store的"SET_QUEST"方法
action2(){ ... }
}
directives: {
'my-directive': {
bind: function(){ //鉤子函數,只調用一次,在指令第一次綁定到元素上時調用 }
update: function(newValue, oldValue) { //鉤子函數,在bind之後以初始值為參數第一次調用,之後每當綁定至變化時調用 }
unbind: function(){ //鉤子函數,只調用一次,在指令從元素上解綁時調用 }
}
}
// 自定義指令,在<template>中以<div v-my-directives = ""> 方式調用
}
</script>
<style> </style>
<template>中放置的是這個頁面(或者頁面的一部分)所擁有的控件,而<script>中定義的是Vue的數據對象和方法,<style>中定義的是控件的css樣式。
在methods中經常使用到“this”關鍵字,該關鍵字指向Vue組件實例。
event.target: 觸發事件的具體控件,不產生冒泡作用,是誰就是誰,這個在鎖定事件觸發的控件時經常用到,比如:
<div @click.stop = "addItem($event)">
<span data-type = "radio">單選題</span>
<span data-type = "checkbox">多選題</span>
<span data-type = "textarea">文本題</span>
</div>
<script>
export default{
method: {
addItem(event){
let target = event.target
if(target.nodeName.toLowerCase() === 'span') { // 當點擊了選擇的按鈕後
this.showMask = true // 顯示彈出框
this.questItem.type = target.dataset.type // 設置問題的類型
}
}
}
</script>
最後講講this.$els: 一個對象,包含注冊有v-el的DOM元素
<div class = "promt-header">
<div>
<label> 問題名稱: </label>
<input type = "text", placeholder = "請輸入標題" v-el: item-title/>
</div>
</div>
<div class = "promt-footer" @click.stop = "handleInput(&event)">
<button type = "button" data-operation = "confirm"> 確定 </button>
<button type = "button" data-operation = "cancel"> 取消 </button>
</div>
<script>
methods: {
handleInput(event) {
let target = event.target
if(target.nodeName.toLowerCase() !== 'button') {
return
}
let itemTitle = this.$els.itemTitle
let itemSelections = this.$els.itemSelections
if(target.dataset.operation === "confirm") {
if(this.questItem.type === "textarea") {
this.addTextarea(itemTitle)
} else {
this.addSelections(itemTitle, itemSelections)
}
} else {
this.handleCancel()
}
},
}
</script>
上面的代碼是不完整的,但是可以看到,v-el把該控件掛載在一個名字為"item-title"的實體中,我們可以通過this.$els.itemTitle將其提取出來
要使用該控件的屬性值(輸入值),可以這樣:
this.$els.itemTitle.value
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持。