在團隊帶人,突然被人問到輪播圖如何實現,進入前端領域有一年多了,但很久沒自己寫過,一直是用大牛寫的插件,今天就寫個簡單的適合入門者學習的小教程。當然,輪播圖的實現原理與設計模式有很多種,我這裡講的是用面向過程函數式編程去實現,相對於面向對象設計模式,代碼難免會顯得臃腫冗余。但沒有面向對象的抽象卻很適合新手理解與學習。已經在BAT的同學看到希望少噴點。另外可以多提意見。
輪播圖的原理:
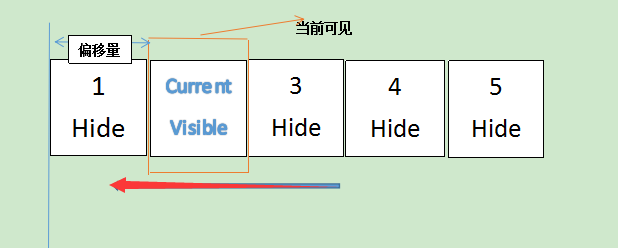
一系列的大小相等的圖片平鋪,利用CSS布局只顯示一張圖片,其余隱藏。通過計算偏移量利用定時器實現自動播放,或通過手動點擊事件切換圖片。
Html布局
首先父容器container存放所有內容,子容器list存在圖片。子容器buttons存放按鈕小圓點。
<div id="container">
<div id="list" style="left: -600px;">
<img src="img/5.jpg" alt="1" />
<img src="img/1.jpg" alt="1" />
<img src="img/2.jpg" alt="2" />
<img src="img/3.jpg" alt="3" />
<img src="img/4.jpg" alt="4" />
<img src="img/5.jpg" alt="5" />
<img src="img/1.jpg" alt="5" />
</div>
<div id="buttons">
<span index="1" class="on"></span>
<span index="2"></span>
<span index="3"></span>
<span index="4"></span>
<span index="5"></span>
</div>
<a href="javascript:;" id="prev" class="arrow"><</a>
<a href="javascript:;" id="next" class="arrow">></a>
</div>
優化,無縫滾動。
當你從最後一張圖切換回第一張圖時,有很大空白,利用兩張輔助圖來填補這個空白。
這裡補充下無縫滾動,直接看代碼,復制最後一張圖片放置第一張圖片前,同時復制第一張圖片放置最後一張圖片的後面。並且,將第一張圖片輔助圖(實際上是實際顯示的第5張圖片隱藏起來,故設置style="left: -600px;")
CSS修飾
1、對盒子模型,文檔流的理解,絕對定位問題。
2、注意list的overflow:hidden;只顯示窗口的一張圖片,把左右兩邊的都隱藏起來。
3、確保buttons中每個span所在層置頂,將其設置為最頂端。(z-index:999)
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
text-decoration: none;
}
body {
padding: 20px;
}
#container {
width: 600px;
height: 400px;
border: 3px solid #333;
overflow: hidden;
position: relative;
}
#list {
width: 4200px;
height: 400px;
position: absolute;
z-index: 1;
}
#list img {
width: 600px;
height: 400px;
float: left;
}
#buttons {
position: absolute;
height: 10px;
width: 100px;
z-index: 2;
bottom: 20px;
left: 250px;
}
#buttons span {
cursor: pointer;
float: left;
border: 1px solid #fff;
width: 10px;
height: 10px;
border-radius: 50%;
background: #333;
margin-right: 5px;
}
#buttons .on {
background: orangered;
}
.arrow {
cursor: pointer;
display: none;
line-height: 39px;
text-align: center;
font-size: 36px;
font-weight: bold;
width: 40px;
height: 40px;
position: absolute;
z-index: 2;
top: 180px;
background-color: RGBA(0, 0, 0, .3);
color: #fff;
}
.arrow:hover {
background-color: RGBA(0, 0, 0, .7);
}
#container:hover .arrow {
display: block;
}
#prev {
left: 20px;
}
#next {
right: 20px;
}
Js
首先我們先實現出手動點擊左右兩個箭頭切換圖片的效果:
window.onload = function() {
var list = document.getElementById('list');var prev = document.getElementById('prev');
var next = document.getElementById('next');
function animate(offset) {
//獲取的是style.left,是相對左邊獲取距離,所以第一張圖後style.left都為負值,
//且style.left獲取的是字符串,需要用parseInt()取整轉化為數字。
var newLeft = parseInt(list.style.left) + offset;
list.style.left = newLeft + 'px';
}
prev.onclick = function() {
animate(600);
}
next.onclick = function() {
animate(-600);
}
}
運行後我們會發現,一直點擊右箭頭 ,會出現空白,而且,不能回到第一張圖片。要點擊左箭頭才能回到第一張圖片。
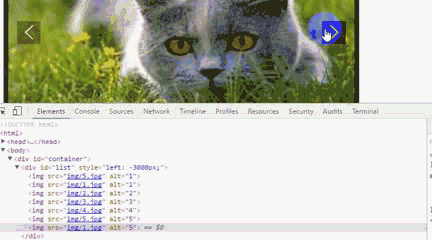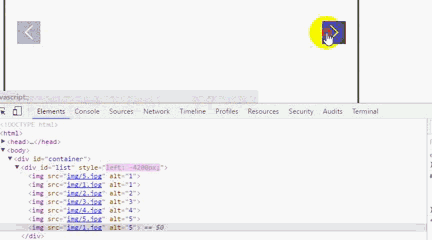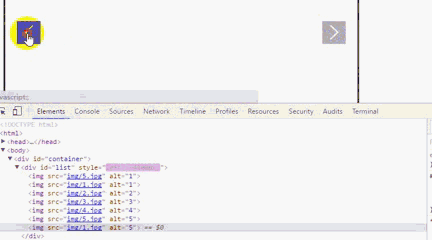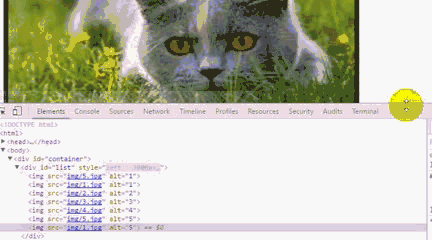
利用谷歌浏覽器F12,原因是我們利用偏移量left來獲取圖片,當看到left值小於3600時,因為沒有第8張圖片就出現空白,所以這裡我們需要對偏移量做一個判斷。
在animate函數裡加上這麼一段:
if(newLeft<-3000){
list.style.left = -600 + 'px';
}
if(newLeft>-600){
list.style.left = -3000 + 'px';
}
好,運行一下,沒問題了。輪播圖,顧名思義,是自己會動的圖片,這個時候我們需要用到浏覽器的內置對象定時器。
對於定時器,有必要說明一下setInterval()跟setTimeout的區別了。簡單來說,setInterval()執行多次,setTimeout()只執行一次。
更具體的用法可以點擊鏈接查看區別:window.setInterval window.setTimeout 。
這裡我們是用setInterval(),因為我們的圖片需要循環滾動。插入下面
var timer;
function play() {
timer = setInterval(function () {
prev.onclick()
}, 1500)
}
play();
運行,ok!
但是,當我們想仔細看某一張圖片時候,要把圖片停住,我們清楚定時器就可以了,這裡用到window.clearInterval 這個方法。
這裡,我們需要對其DOM操作,需要獲取整個輪播圖區域;
var container = document.getElementById('container');
function stop() {
clearInterval(timer);
}
container.onmouseover = stop;
container.onmouseout = play;
但這裡,一個輪播圖基本算完成了,有同學·會問,那麼簡單。看到圖片下面的那一排小圓點沒。我給你加功能了。
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
這裡是升級版:
var buttons = document.getElementById('buttons').getElementsByTagName('span');
var index = 1;
function buttonsShow() {
//這裡需要清除之前的樣式
for (var i = 0; i < buttons.length; i++) {
if (buttons[i].className == 'on') {
buttons[i].className = '';
}
}
//數組從0開始,故index需要-1
buttons[index - 1].className = 'on';
}
prev.onclick = function() {
index -= 1;
if (index < 1) {
index = 5;
}
buttonsShow();
animate(600);
}
next.onclick = function() {
//由於上邊定時器的作用,index會一直遞增下去,我們只有5個小圓點,所以需要做出判斷
index += 1;
if (index > 5) {
index = 1;
}
buttonsShow();
animate(-600);
}

現在看起來正常多了吧,但我們想實現通過鼠標任意點擊其中一個小圓點,切換到相應的圖片,原理同樣,我們還是需要通過偏移量去找到對應的圖片。
for (var i = 0; i < buttons.length; i++) {
buttons[i].onclick = function() {
//優化,當前圖片點擊當前的小圓點不執行以下代碼。
if (this.className == "on") {
return;
}
/* 偏移量獲取:這裡獲得鼠標移動到小圓點的位置,用this把index綁定到對象buttons[i]上,去谷歌this的用法 */
/* 由於這裡的index是自定義屬性,需要用到getAttribute()這個DOM2級方法,去獲取自定義index的屬性*/
var clickIndex = parseInt(this.getAttribute('index'));
var offset = 600 * (clickIndex - index);
animate(offset);
//存放鼠標點擊後的位置,用於小圓點的正常顯示
index = clickIndex;
buttonsShow();
}
}

大家,可能發現了,這個輪播圖有點奇怪,不中規中矩,它是向左切換的,改寫一下:
function play() {
//將輪播圖換成向右切換圖片
timer = setInterval(function () {
next.onclick();
}, 2000)
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
text-decoration: none;
}
body {
padding: 20px;
}
#container {
width: 600px;
height: 400px;
border: 3px solid #333;
overflow: hidden;
position: relative;
}
#list {
width: 4200px;
height: 400px;
position: absolute;
z-index: 1;
}
#list img {
width: 600px;
height: 400px;
float: left;
}
#buttons {
position: absolute;
height: 10px;
width: 100px;
z-index: 2;
bottom: 20px;
left: 250px;
}
#buttons span {
cursor: pointer;
float: left;
border: 1px solid #fff;
width: 10px;
height: 10px;
border-radius: 50%;
background: #333;
margin-right: 5px;
}
#buttons .on {
background: orangered;
}
.arrow {
cursor: pointer;
display: none;
line-height: 39px;
text-align: center;
font-size: 36px;
font-weight: bold;
width: 40px;
height: 40px;
position: absolute;
z-index: 2;
top: 180px;
background-color: RGBA(0, 0, 0, .3);
color: #fff;
}
.arrow:hover {
background-color: RGBA(0, 0, 0, .7);
}
#container:hover .arrow {
display: block;
}
#prev {
left: 20px;
}
#next {
right: 20px;
}
</style>
<script type="text/javascript">
/* 知識點: */
/* this用法 */
/* DOM事件 */
/* 定時器 */
window.onload = function () {
var container = document.getElementById('container');
var list = document.getElementById('list');
var buttons = document.getElementById('buttons').getElementsByTagName('span');
var prev = document.getElementById('prev');
var next = document.getElementById('next');
var index = 1;
var timer;
function animate(offset) {
//獲取的是style.left,是相對左邊獲取距離,所以第一張圖後style.left都為負值,
//且style.left獲取的是字符串,需要用parseInt()取整轉化為數字。
var newLeft = parseInt(list.style.left) + offset;
list.style.left = newLeft + 'px';
//無限滾動判斷
if (newLeft > -600) {
list.style.left = -3000 + 'px';
}
if (newLeft < -3000) {
list.style.left = -600 + 'px';
}
}
function play() {
//重復執行的定時器
timer = setInterval(function () {
next.onclick();
}, 2000)
}
function stop() {
clearInterval(timer);
}
function buttonsShow() {
//將之前的小圓點的樣式清除
for (var i = 0; i < buttons.length; i++) {
if (buttons[i].className == "on") {
buttons[i].className = "";
}
}
//數組從0開始,故index需要-1
buttons[index - 1].className = "on";
}
prev.onclick = function () {
index -= 1;
if (index < 1) {
index = 5
}
buttonsShow();
animate(600);
};
next.onclick = function () {
//由於上邊定時器的作用,index會一直遞增下去,我們只有5個小圓點,所以需要做出判斷
index += 1;
if (index > 5) {
index = 1
}
animate(-600);
buttonsShow();
};
for (var i = 0; i < buttons.length; i++) {
buttons[i].onclick = function () {
//優化,當前圖片點擊當前的小圓點不執行以下代碼。
if (this.className == "on") {
return;
}
/* 這裡獲得鼠標移動到小圓點的位置,用this把index綁定到對象buttons[i]上,去谷歌this的用法 */
/* 由於這裡的index是自定義屬性,需要用到getAttribute()這個DOM2級方法,去獲取自定義index的屬性*/
var clickIndex = parseInt(this.getAttribute('index'));
var offset = 600 * (clickIndex - index); //這個index是當前圖片停留時的index
animate(offset);
index = clickIndex; //存放鼠標點擊後的位置,用於小圓點的正常顯示
buttonsShow();
}
}
container.onmouseover = stop;
container.onmouseout = play;
play();
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="container">
<div id="list" style="left: -600px;">
<img src="img/5.jpg" alt="1"/>
<img src="img/1.jpg" alt="1"/>
<img src="img/2.jpg" alt="2"/>
<img src="img/3.jpg" alt="3"/>
<img src="img/4.jpg" alt="4"/>
<img src="img/5.jpg" alt="5"/>
<img src="img/1.jpg" alt="5"/>
</div>
<div id="buttons">
<span index="1" class="on"></span>
<span index="2"></span>
<span index="3"></span>
<span index="4"></span>
<span index="5"></span>
</div>
<a href="javascript:;" id="prev" class="arrow"><</a>
<a href="javascript:;" id="next" class="arrow">></a>
</div>
</body>
</html>
點擊
over
最後,我們完成了一個簡單的輪播圖,在我的 Github 裡可以找到源碼。覺得不錯就star一下。
- 上一頁:JS 事件冒泡整理 浏覽器的事件流
- 下一頁:JS實現簡單倒計時